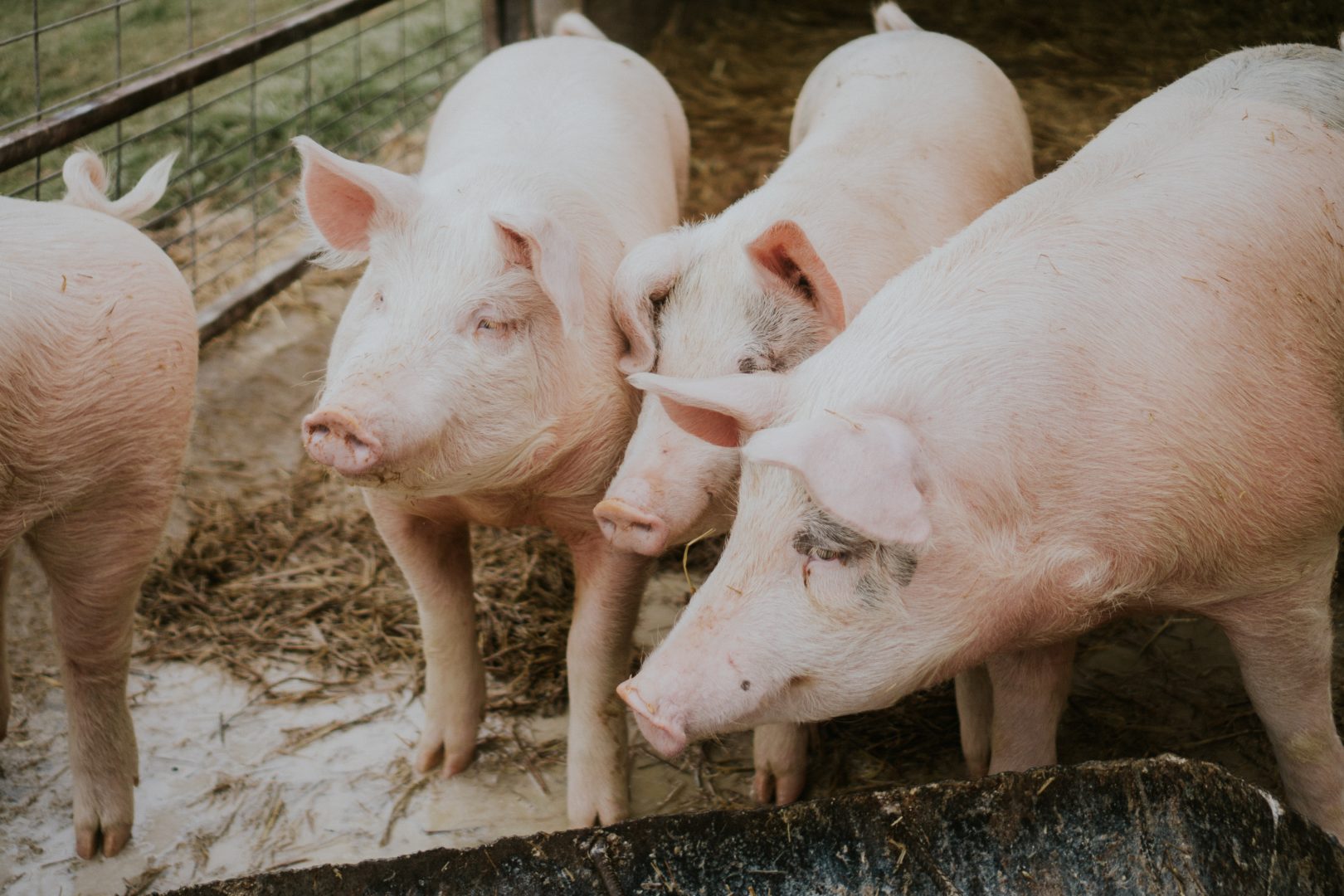
In our previous editions of “Making a Difference” we’ve looked at topics including “Animal Welfare”, “Needle fragments” left in the meat, “Environmental Impact” of discarded needles, “User Safety”, “Set back costs”, and improved “Vaccine utilization”. In our final edition of the year we want of explore the potential of “ID” (Inter-Dermal or Intra-Dermal) injections.
What is an “ID” (Inter-Dermal or Intradermal) injection? Here’s what Wikipedia says:
Intradermal injection is the injection of a substance into the dermis, just below the epidermis. This route has the longest absorption time as compared to subcutaneous injections and intramuscular injections.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intradermal_injection
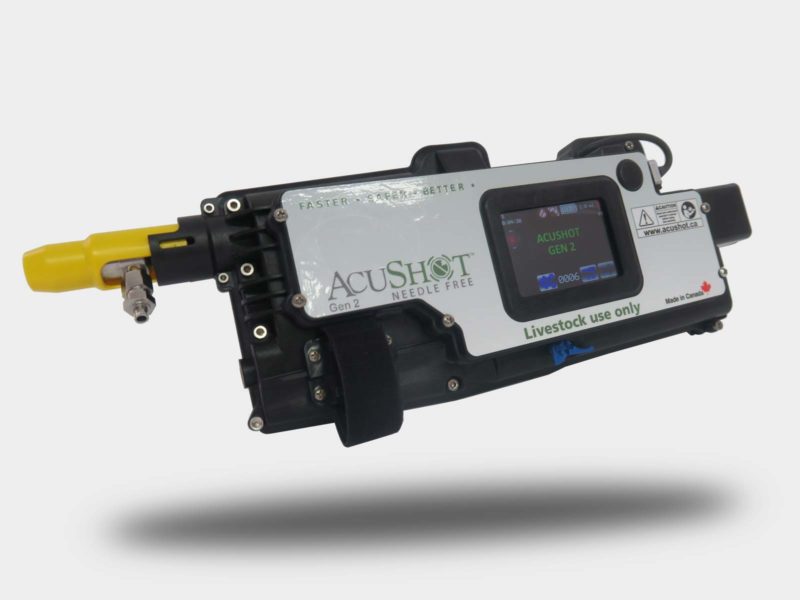
Although Needle-Free technology is still early in its adoption phase, interest in this disruptive technology is growing. Livestock producers, Food processors, Veterinarians, Pharmaceutical companies and many other industry partners are expressing interest in adopting Needle-Free technology into their enterprise. Along with its ability perform traditional IM and SQ injections, perhaps the greatest optimism lies in the AcuShot’s ability to accurately perform “ID” injections.
So…why the interest in “ID” injections? Here’s what the World Health Organization has to say:
Most vaccines are delivered by the intramuscular or subcutaneous routes using a needle and syringe; the intradermal route is only widely used for the administration of Bacille Calmette-Guérin and rabies vaccines. However there is renewed interest in intradermal vaccine delivery, driven by the fact that the dermis and epidermis of human skin are rich in antigen-presenting cells, suggesting that delivery of vaccines to these layers, rather than to muscle or subcutaneous tissue, should be more efficient and induce protective immune responses with smaller amounts of vaccine antigen. http://www.who.int/bulletin/volumes/89/3/10–079426/en/
What many people don’t know is that “ID” injections occur passively every time you use an AcuShot NeedleFree injector because a small amount of the vaccine is left in the skin of the animal on each and every injection. Add to that the fact that several trials conducted by leading pharmaceutical companies using AcuShot Needle Free have proven its ability to consistently apply “ID” injections as low as 0.2ML. All this means the future of “ID” injections using AcuShot’s industry leading Needle-Free technology looks bright.
As we see a move to adoption of “ID” injections using AcuShot Needle Free, we will continue to see improved vaccine utilization, further reduction in stress to animals and improved biological and economic performance.
Broad adoption of “ID” injections was a key reason for the development of AcuShot’s innovative second generation Needle-Free technology.
View actual on-farm injection videos at www.acushot,ca and see for yourself how effective our device really is.